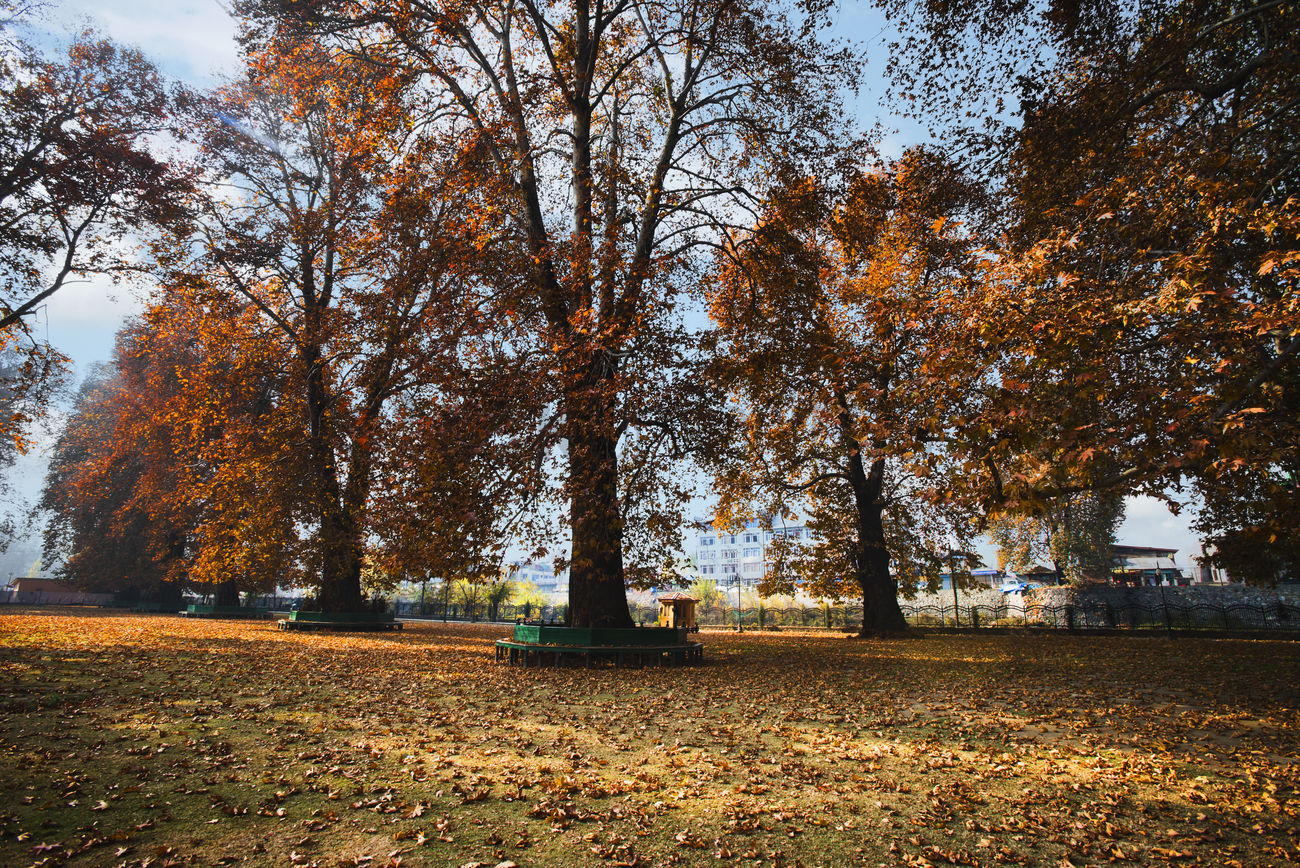
Srinagar:The J&K Forest Department, in collaboration with the J&K Forest Research Institute, has initiated a GIS-based, QR-enabled conservation project for the iconic chinar tree.
This initiative aims to safeguard chinar trees from threats such as urbanisation, deforestation, and habitat degradation, officials said.
They said the project, spearheaded by the Research Forest Division Srinagar, involves geotagging and QR coding of chinar trees to enable precise monitoring and management.
“By leveraging digital tools, the initiative seeks to ensure the long-term survival of this heritage species, which holds immense cultural and historical significance for the Kashmir Valley,” they said.
“Chinar trees are a living testament to our heritage, but urban expansion and habitat loss have put them at risk. This initiative is our way of securing their future,” the officials added.
The geotagging process maps the exact locations of chinar trees across the region, creating a comprehensive database for their management. QR codes attached to each chinar tree provide detailed information about its health, age, and growth patterns, enabling researchers and conservationists to track changes over time.
“Through geotagging and QR technology, we aim to create a robust system for monitoring these trees and addressing threats proactively,” said senior scientist Dr Tariq Bhat from the J&K Forest Research Institute.
Dr Bhat further stated that the initiative also aims to raise public awareness about the significance of chinar trees and encourage community participation in their preservation.
“The QR codes provide accessible information, allowing residents and visitors to learn about the trees’ ecological and cultural value,” he added. (KNT)